Our existing urban drainage systems are being asked to do far more than they were ever designed for. Denser development, hard landscaping, population growth and increasingly intense rainfall are combining to expose a fundamental weakness in traditional sewer networks.
The symptoms are now familiar: surface water flooding that appears without warning, wastewater assets pushed beyond capacity, and combined sewer overflows releasing polluted water into rivers and coastal environments.
This is not a marginal problem, and it is not going away. The question is whether the response should focus on large-scale infrastructure expansion, or whether a more adaptable approach is both more effective and more feasible.
Rethinking capacity through smarter water management
There is an alternative to large-scale remodelling of traditional drainage infrastructure, and it lies in re-framing how stormwater is managed at multiple points across towns and cities. Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) offer a way to intercept, slow and treat water before it ever reaches the sewer. When deployed widely, individual SuDS features work collectively to deliver a level of performance that far exceeds what any single intervention could achieve alone.
Crucially, this is not about simply adding volume, it is about distributing control. Nature-based drainage solutions can reduce pressure on existing networks while also delivering environmental and social gains that conventional underground assets do not provide.
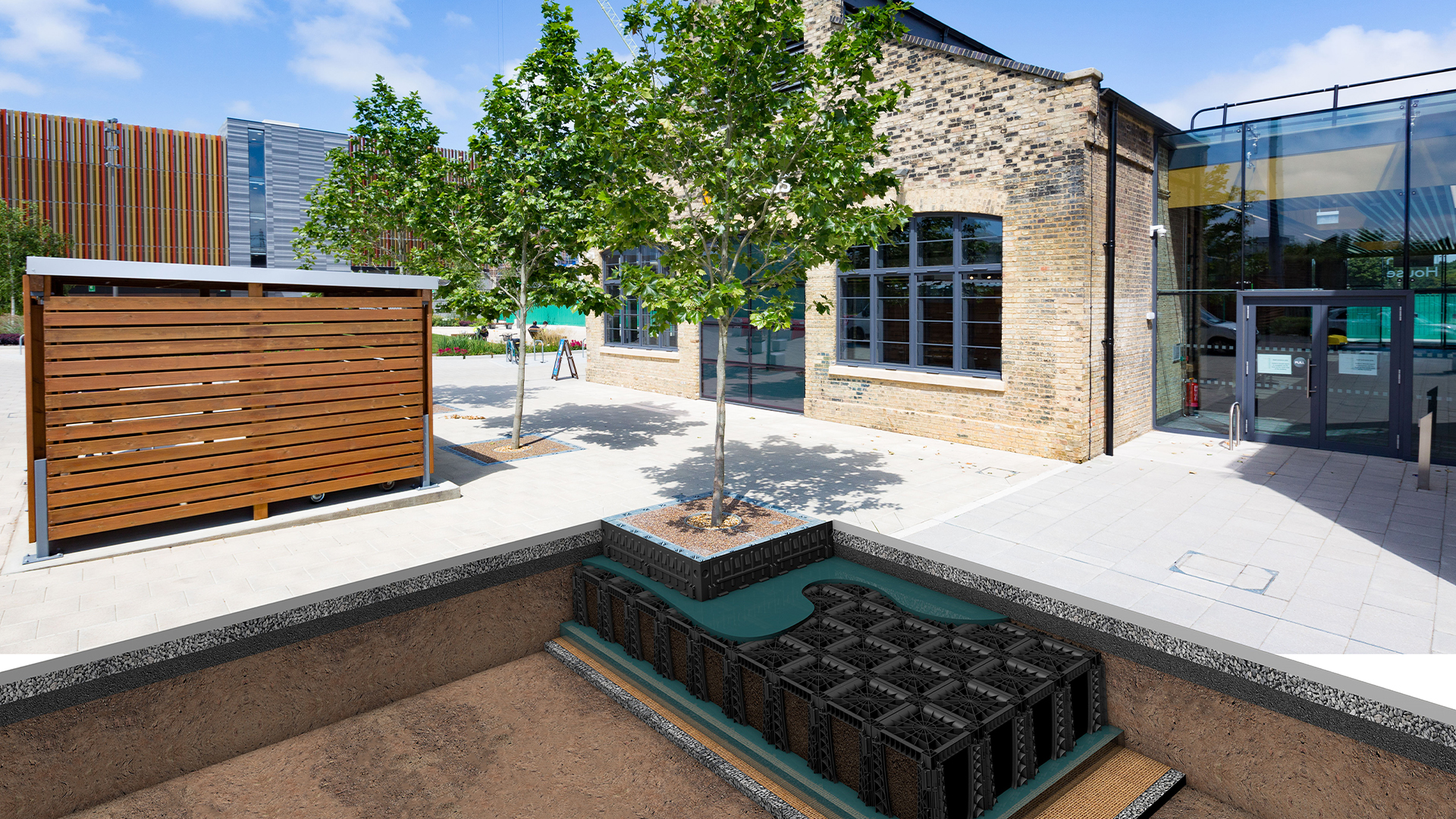

Why scale matters
Small, well-placed SuDS components – including permeable surfaces, rain gardens, planters and engineered tree pits – can make a substantial difference when implemented across a catchment rather than as isolated gestures. By managing rainfall close to where it lands, these systems prevent rapid runoff from overwhelming downstream infrastructure.
The benefits of this approach are wide-ranging:
- Lower flood exposure
By retaining and slowing runoff at source, dispersed SuDS features reduce the likelihood of surface water accumulating in vulnerable locations. - Cleaner receiving waters
Filtration and natural treatment processes remove pollutants before they are carried into rivers, streams and coastal waters. - Rapid delivery with minimal disruption
Compared to major drainage upgrades, SuDS installations are quicker to implement and far less intrusive for surrounding communities. - Stronger urban ecosystems
Vegetated systems create habitat and support pollinators and other species, improving ecological resilience in built environments. - Improved public realm
Green infrastructure contributes to cooler, more attractive streets and public spaces, enhancing comfort and liveability.
From concept to evidence
The performance of SuDS is no longer hypothetical. Systems developed by specialist hydraulic engineers have been independently assessed and shown to manage meaningful storm events reliably over time.
One such example is SuDSPod, which has been subject to evaluation through EUGINE (Enhancing Urban Green Infrastructure via kNowledge Exchange), a joint initiative involving the University of Sheffield and Severn Trent Water. Interim findings from this programme have identified SuDSPod as an effective attenuation solution at the building downpipe scale.
Testing showed that the unit significantly reduced peak flow rates, achieving attenuation of up to 5.9l/min from a 46.5m² contributing area during an M10-240 rainfall scenario. Performance remained stable throughout the four-month trial, with no maintenance issues recorded. In parallel, the system’s hydraulic model was verified against observed data, confirming its accuracy in predicting flow behaviour.
Together, these results demonstrate that SuDSPod can provide dependable, low-maintenance stormwater control, suitable for repeated deployment in areas where sewer networks require relief to reduce surface water flooding and limit CSO events.
Selecting SuDS products manufactured in the UK brings additional advantages beyond hydraulic performance, too. Shorter supply chains reduce transport emissions, while the use of recycled materials, collaboration with regional installers and investment in British manufacturing contribute measurable social value alongside drainage improvement.
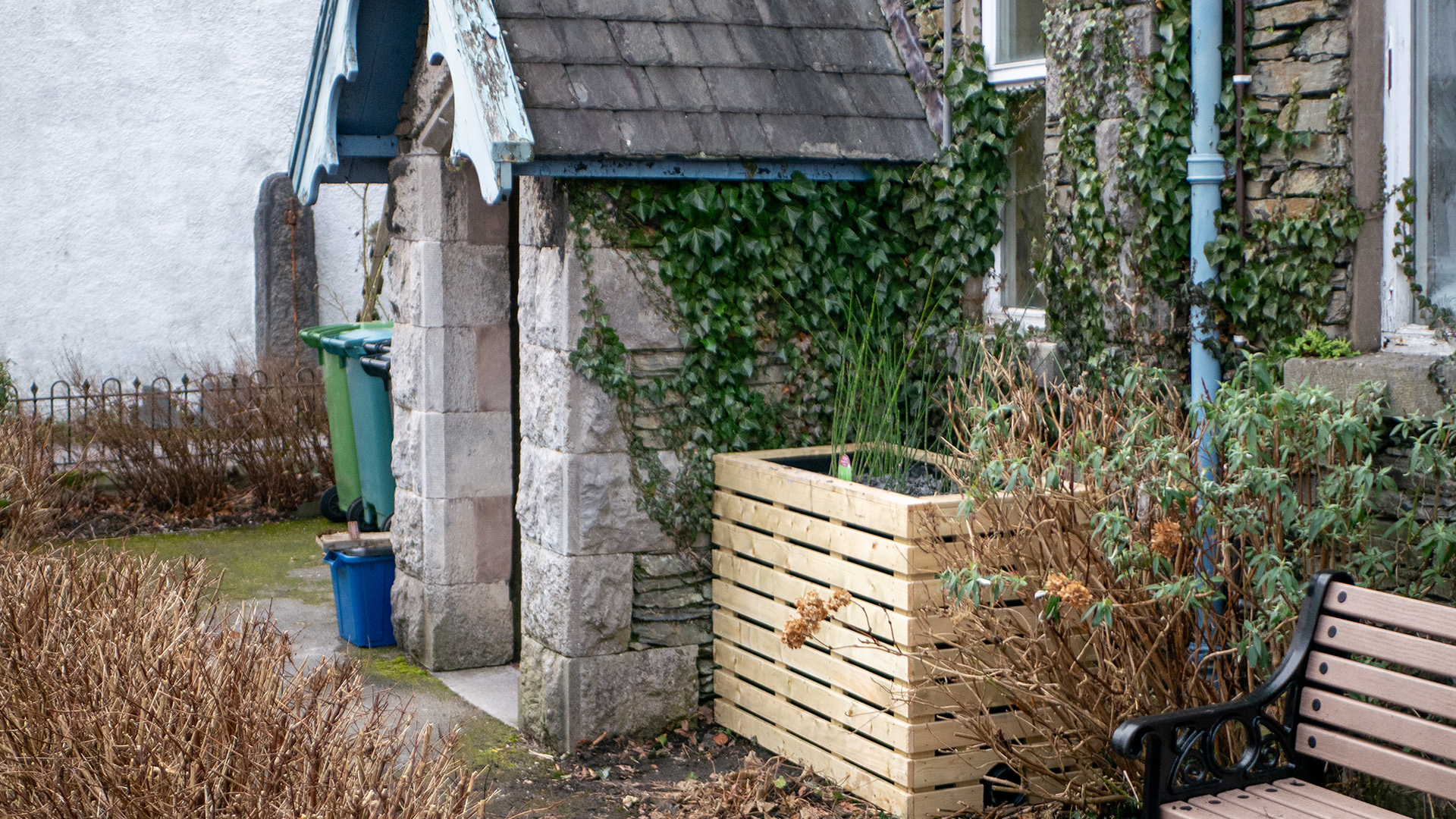

Building resilience through repetition
Long-term urban flood resilience will not be delivered through occasional flagship schemes. It will come from embedding modest, repeatable SuDS interventions throughout streets, developments and public spaces, creating a distributed system that works continuously and collectively.
In this context, SuDS are not an optional enhancement. They are an essential component of climate-ready infrastructure.