Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) are a set of design principles and practices that aim to manage and control surface water runoff in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner. SuDS are designed to mimic natural drainage processes and reduce the impact of urbanisation on the water cycle. They provide an alternative to traditional drainage systems that focus on collecting and rapidly discharging rainwater into underground pipes.
The primary function of SuDS is to manage and control the quantity and quality of stormwater runoff, thus reducing the risk of flooding and improving water quality. SuDS employs a combination of techniques and components that help slow down, store, and treat rainwater at or near its source. Key functions are often referred to as the Stormwater management train. Include:
Source Control:
SuDS focus on managing rainwater as close to its source as possible. This involves intercepting rainwater runoff before it enters the conventional piped drainage systems.
Source control measures include techniques like permeable surfaces, tree pits, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting, which allow rainwater to infiltrate or be stored on-site.
Conveyance Control:
SuDS aim to control the flow and conveyance of stormwater by using techniques that attenuate the runoff and prevent rapid and excessive flow into the drainage network.
Examples of conveyance control measures include swales, open channels, and flow restrictors that slow down the flow of water, allowing it to infiltrate or be stored for later use.
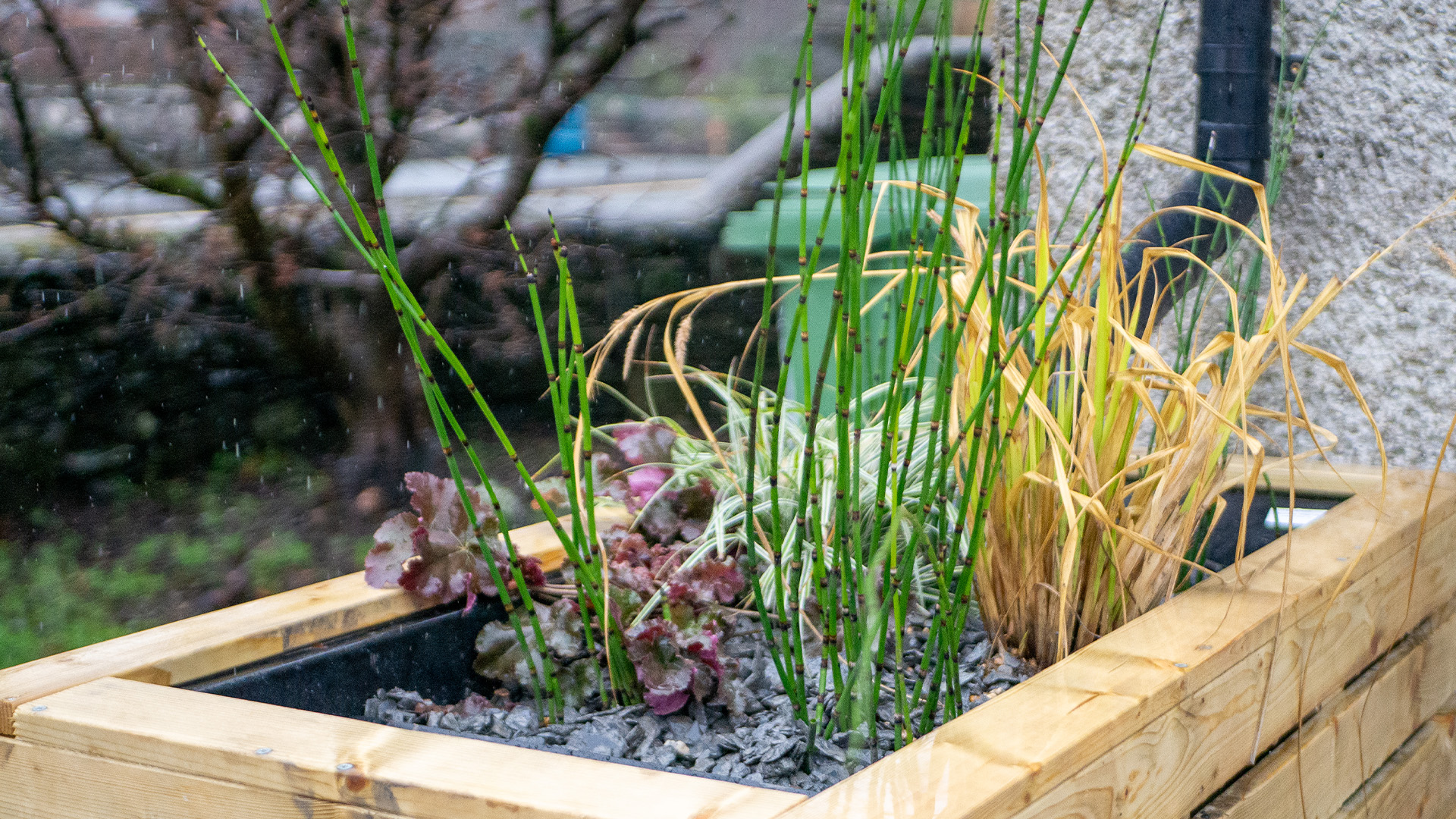

Attenuation:
SuDS include features that attenuate or manage the volume of stormwater runoff. This helps to reduce the peak flow rates and minimize the risk of downstream flooding.
Techniques such as tree pits, detention basins, ponds, and underground storage tanks are used to store excess water temporarily until it can be released slowly into the drainage system or allowed to infiltrate into the ground.
Treatment:
SuDS incorporate elements that treat stormwater to improve its quality before it is discharged into natural watercourses or water bodies.
Treatment measures include the use of filtration systems, vegetated swales, and constructed wetlands that remove pollutants and sediments from the runoff, improving water quality.
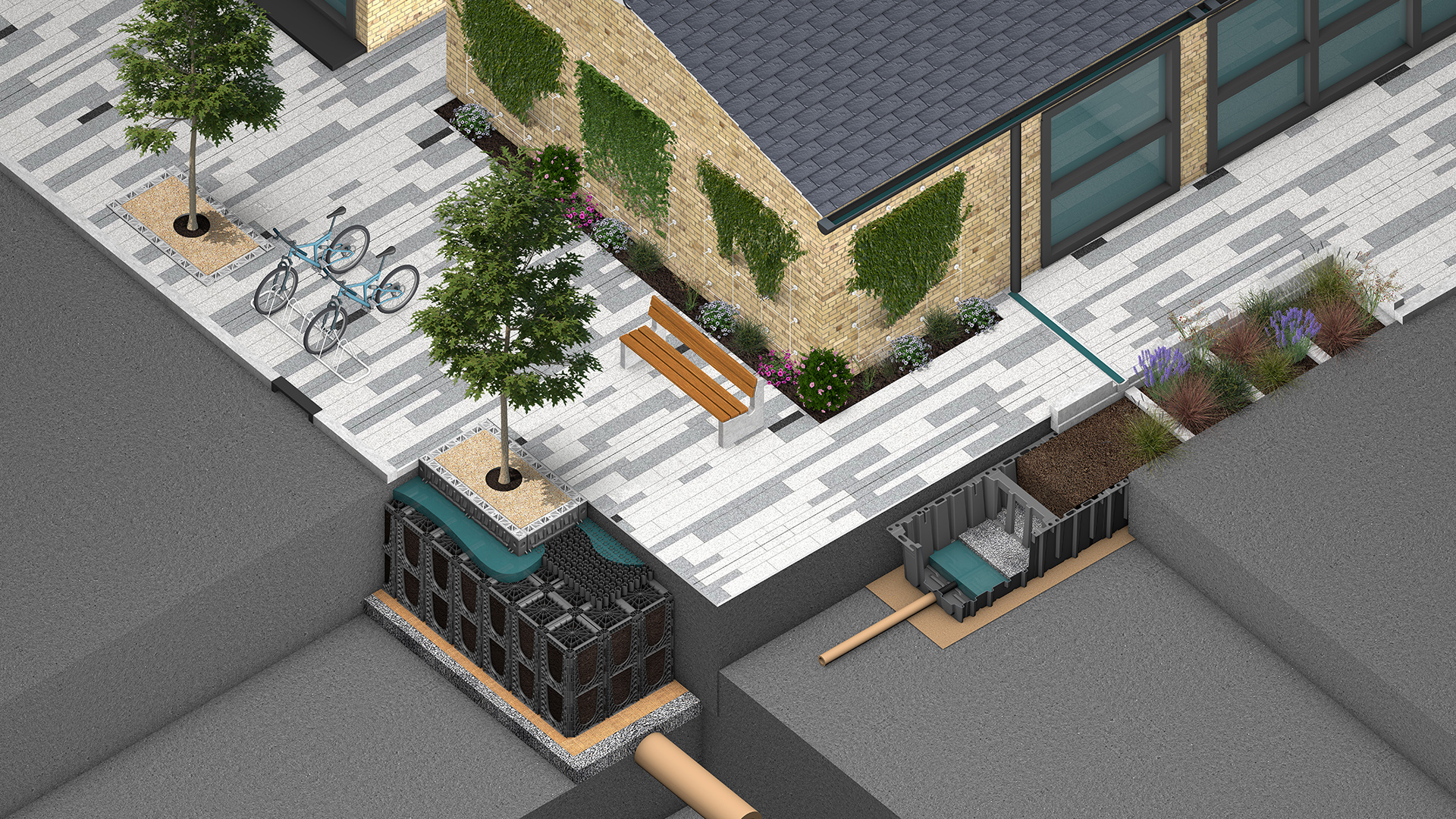

SuDS Design Considerations
Site assessment and suitability for SuDS implementation are essential to ensure that the chosen drainage strategies align with the site’s characteristics, environmental considerations, and flood risk management needs. Water resource management goals should align with regulatory requirements and ensure climate change resilience.
Design options for managing surface water runoff, include permeable pavements, tree pits, raingardens, above ground planters, swales, ponds, and basins.
The types of benefits will vary depending on the site, however broadley fit into four categories: Water quantity, water quality, amenity, and biodiversity. GreenBlue Urban offer full support from design to implementation with the following MicroSuDS Solutions:-
Urban Tree Pits
Tree pits are a popular and effective SuDS intervention, especially in urban areas where space may be limited. They combine the benefits of stormwater management, water quality improvement, urban cooling, and ecological enhancement, making them a valuable addition to sustainable drainage strategies.
Rain Gardens
A raingarden is a shallow, planted depression designed to capture, infiltrate, and treat rainwater from impervious surfaces such as roofs, driveways, and roads.
Rain gardens are designed to be both functional and aesthetically pleasing, providing multiple benefits for stormwater management, water quality improvement, groundwater recharge, erosion control, and habitat creation. They are an effective and sustainable approach to managing rainwater runoff in both residential and commercial settings.
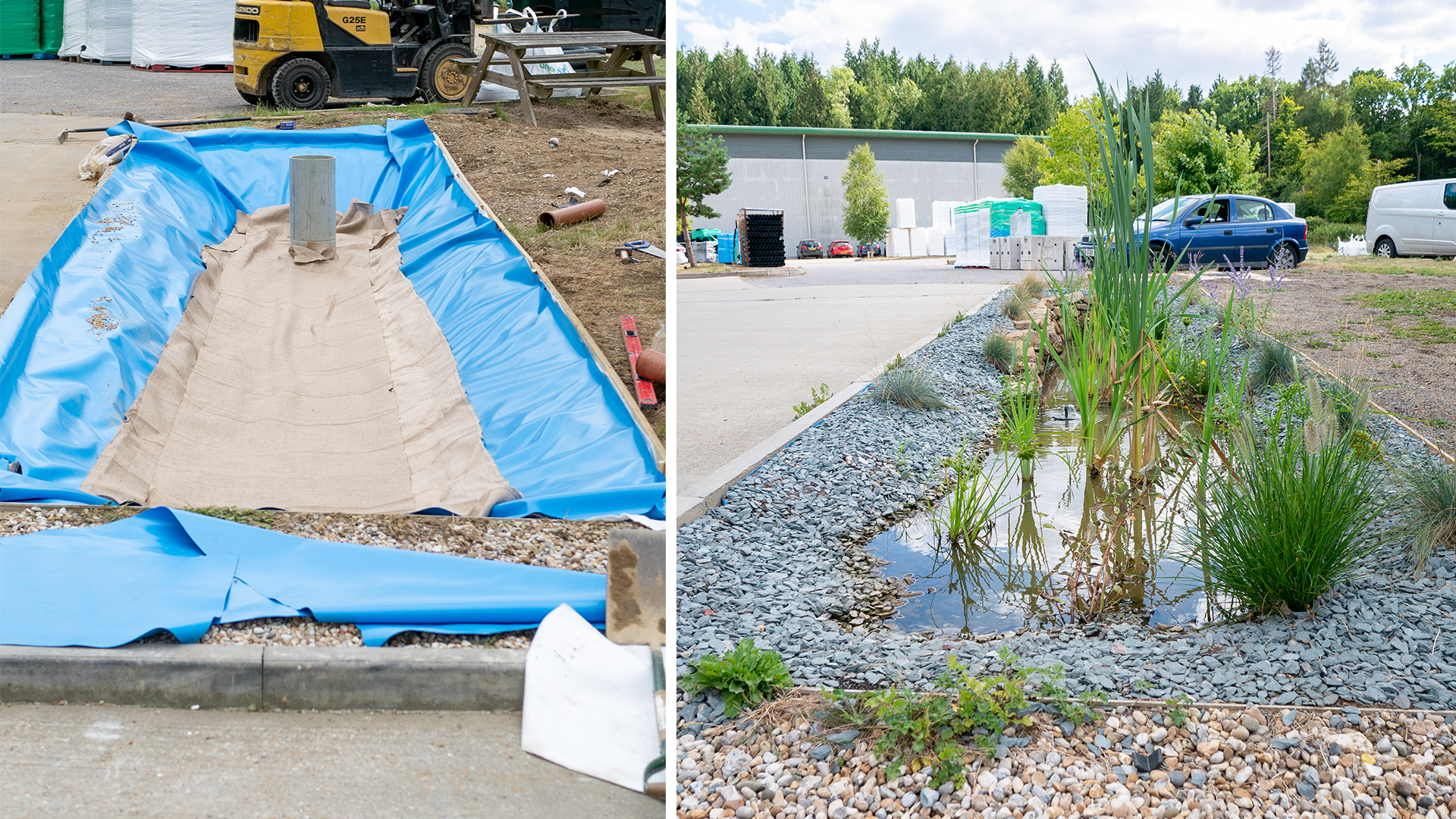

An above-ground planter, such as the SuDSPod, can significantly contribute to stormwater attenuation through increased infiltration and storage through the soil medium, slowing peak flow rates. In densely populated urban areas, above-ground planters provide a space-efficient solution for stormwater management, utilising space without requiring significant ground area.
Overall, SuDS function by mimicking natural water management processes, reducing the impact of urban development on the water cycle, and promoting sustainable and responsible management of stormwater. By implementing SuDS techniques, towns and cities can reduce the risk of flooding, enhance water quality, create habitats, and contribute to the overall resilience and sustainability of urban environments.