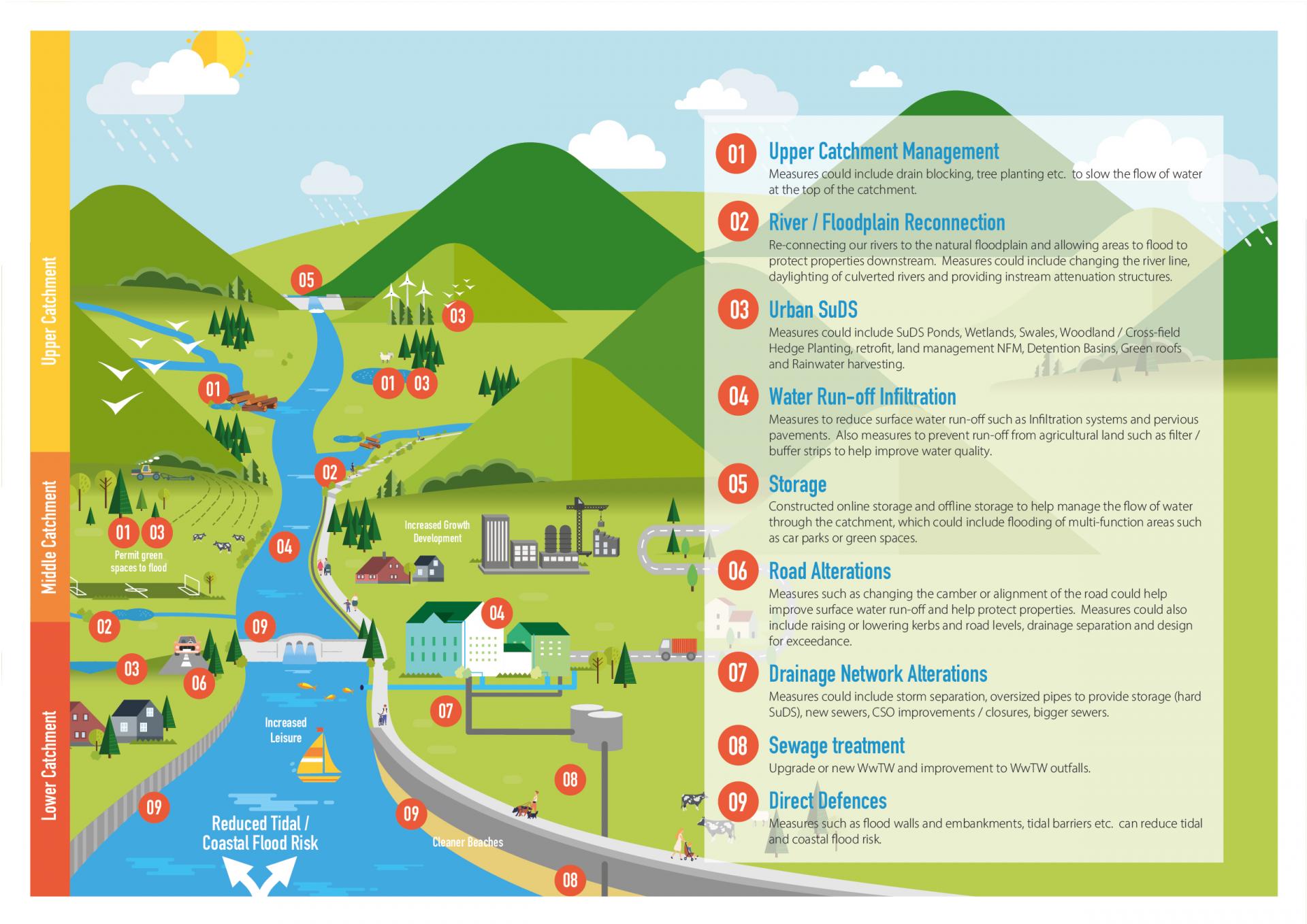
The preservation of water quality and the protection of biodiversity are two critical aspects of modern urban development. As our towns and cities expand, as new housing and commercial developments emerge, the strain on natural resources and ecosystems becomes more pronounced. Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) offer an innovative and effective way to address both water quality issues and the conservation of biodiversity.

Assessment of Pollution Control Devices
Assessing pollution control devices is a pivotal step in ensuring the efficacy of SUDS in managing water quality. Various elements need to be considered during the assessment:
Performance: The efficiency of pollution control devices, such as vegetated swales, basins, rain gardens, tree pits, and permeable pavements, in reducing pollutants from runoff should be measured. Regular monitoring and evaluation help identify potential issues and provide opportunities for improvements.
Longevity: The durability and lifespan of these devices are crucial for sustained water quality improvement. Using high-quality materials and proper maintenance can extend their functional lifespan. They should work harmoniously with the surroundings and enhance the aesthetic appeal of the area.
We asked our industry friend Jo Bradley of Stormwater Shepherds “How can we design for long-term water quality success with a focus on biodiversity and wildlife”.
Good water quality treatment in SuDS relies on the opportunity for effective sedimentation of solids, in a sediment removal device, a chamber, a basin or a pond. Anything that allows the stormwater to rest awhile will do, so that the sediment can settle out, taking with it many of the particulate pollutants and those that piggyback on them.
Good sedimentation will remove a decent proportion of the pollutants and protect the downstream devices so that they can be healthy habitats for wildlife. But remember that sedimentation devices need to be maintained so that they carry on working well.
The other part of water quality treatment usually relies on the provision of layers of aerated soils with some organic matter to create a healthy population of micro-organisms; these organisms will break down the residual pollutants so that they can be degraded or taken up by plants and trees.
Some of the pollutants will be captured in the soil too, where the micro-organisms can take their time to break down the more troublesome chemicals. These devices can all contribute to the creation of a living-breathing ecosystem at the centre of the SuDS scheme which creates the best opportunity for nature to manage pollution and to protect our planet.
Implementing Good Design for Long-Term Success
Implementing SUDS for water quality improvement and biodiversity conservation requires a thoughtful and comprehensive approach:
Site-Specific Design: Every development is unique, and SUDS should be tailored to the site’s characteristics. Factors like soil type, slope, and existing vegetation play a significant role in determining the most effective SUDS components.
Natural Processes: Design SUDS to mimic natural hydrological cycles. Incorporate features like vegetated swales and wetlands that help filter pollutants and promote groundwater recharge.
Maintenance Considerations: Develop a maintenance plan that outlines regular inspections, cleaning schedules, and repairs. Engage community members and stakeholders to foster a sense of ownership and responsibility.

Promoting Biodiversity and Wildlife
SUDS serve as a vital tool for enhancing local biodiversity and supporting wildlife:
Native Vegetation: Incorporate native plants and trees in SUDS design. These species are adapted to the local ecosystem, require less maintenance, and provide habitats and food sources for wildlife.
Wildlife-Friendly Features: Design elements such as wildlife ponds, green roofs, and bird boxes can attract a diverse range of species, from insects to birds.
Habitat Connectivity: Plan the layout of SUDS components to create green corridors that allow wildlife to move through the landscape safely.

Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) are not merely a technical solution to water quality issues; they embody a holistic approach that integrates effective pollution control, innovative design, and biodiversity conservation. By implementing site-specific designs, regular assessments, and maintenance plans, we can ensure the long-term success of SUDS in both mitigating water pollution and nurturing wildlife.
As we continue to expand our urban spaces, GreenBlue Urban continue to embrace the potential of SUDS innovation has enabled us to enhance our product offering with many new adaptable solutions to market. Enabling you to create harmonious environments where nature is at the heart of every development.